Different types of industrial joystick controls are used in an array of industries. ‘Industrial joystick controls‘ facilitate easy and precise machine interfacing from construction and robotics to manufacturing. Like all types of technologies, industrial joysticks are also constantly evolving. This blog entry will examine industrial joystick controls’ different features and advantages. We will also discuss their impacts on various industries and sectors. Moreover, we will analyze the most recent advances in industrial joysticks technology and how they cater to the changing needs of industries. By the end of the article, you will appreciate the importance of industrial joysticks and modern industrial operations.
What Are the Different Types of Industrial Joysticks?
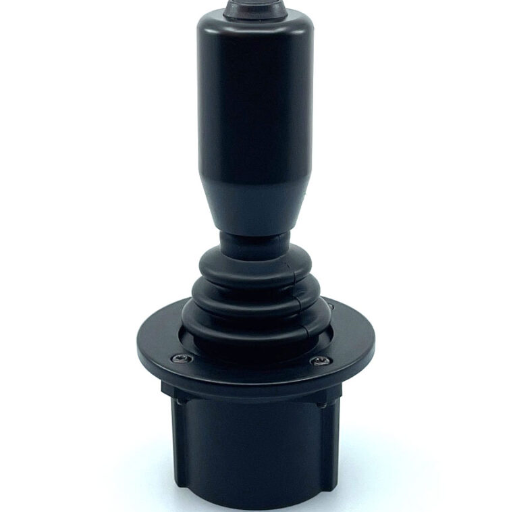

Industrial joysticks are of various types and serve multiple operational functions. They include analog types, which permit continuous variable control, and digital types, which provide on/off or directional input. Multi-axis joysticks allow movement across multiple planes, while miniature joysticks are small and valuable in space-limited areas. Specialized types include finger-operated joysticks for delicate tasks and heavy-duty joysticks for harsh environments. Each joystick type has advantages and disadvantages in application complexity and durability requirements.
Understanding Single-Axis and Multi-Axis Joysticks
Single-axis joysticks only control movement in one directional plane, meaning they can only move forward and backward or left and right. This kind of industrial joystick is used in areas that require a high level of control in a single direction, such as throttle control in industrial machinery or certain vehicle types.
Unlike single-axis joysticks, multi-axis joysticks allow movement in two or even three axes (with rotational movement). They are used in robotics, aviation, and heavy machinery, where control is sophisticated and streamlined. The ability to process several inputs simultaneously allows operators greater adaptability in navigating or operating equipment.
When deciding between single-axis and multi-axis options, consider factors such as the level of control accuracy needed, task difficulty, and available joystick operating space. Multi-axis joysticks are optimal for more complex operations where simultaneous movement in multiple directions is required, while single-axis joysticks are best suited for more simple and direct tasks.
Exploring Hall Effect and Potentiometer Technologies
The basic principles of operation and practical use of Hall Effect and potentiometer Technologies must be considered while evaluating. Sensors using the Hall Effect use magnetic fields to position, thus enabling measurements to be taken at a distance. This further increases the non-contact measurement with minimal wear and tear, making them less durable and more reliable. A potentiometric sensor may be used for rotating and linear position sensor applications.
Due to the Republic of South Africa’s limited disposable income, market demand, and interest, Potentiometers are easier to use in uncomplicated tasks, which makes the Resistive and Movable Wiper-Based Electric Potentiometer popular.
As seen, the technologies have their advantages and disadvantages. All technology has unique attributes that depend on specific external factors, including the environment, expected reliability, precision needed, and set budgets. Embarking on advanced and heavy-duty works makes Hall Effect Joysticks ideal. Other more straightforward, less demanding, and inexpensive projects make bene?ciaries of Pendulum Potentiometer.
The Role of Rocker and Thumb Controls in Industrial Settings
Rocker and thumb controls are crucial for accuracy and productivity in industrial environments. These controls are related to ergonomics in machinery and equipment, requiring operators to provide precise inputs. Rocker-type switches are functional two-way devices that control movements, such as boom arms, conveyor belts, or actuators. Thumb controls are commonly found in joysticks, designed to be controlled by one hand, and offer great adaptability and accessibility.
Compact rockers and thumb controls reduce fatigue and increase comfort and ergonomics for users during prolonged operating periods. Most thumb and rocker controls are constructed with modern techniques to resist harsh environments, including construction, agriculture, or manufacturing. These controls are equally essential in precise, enduring applications. Both types of controls accomplish the same objectives in industrial environments, and their choice depends on detailed operational procedures and the number of control intricacies.
How Do Industrial Joystick Controllers Work?

Industrial joystick controllers translate bodily movements into electronic signals that regulate a machine or system. While operating, the joystick is moved, and its direction and intensity are detected by potentiometers, Hall effect sensors, or even optical encoders. The sensors generate an electric signal proportional to the inflicted input. This signal is sent to the machine’s control system. With such capabilities, the equipment or machines can be accurately controlled, and proper performance and responsiveness are ensured in different industrial applications.
Key Components and Design Features
The components of modern-styled joysticks work together to ensure precision and functionality. The sensors are the key components, providing electrical signals to potentiometers, Hall effect sensors, and optical encoders. Motion detection is crucial for the sensor’s effectiveness, but the gimbal system is equally important. The gimbal system is a significant component of almost all joysticks, twirling smoothly on the axis. Most joysticks today have springs, dampers, or both, allowing the gimbal to rotate around the center point easily.
With an ergonomic approach, sculptured handles, buttons placed on the right spot, non-slip surfaces, and new, durable materials allow the joystick to withstand industrial conditions, make the instruments more comfortable, and prevent fatigue throughout long work hours. The ability to withstand harsh conditions increases the product’s life and joins multiple modern innovations that improve efficiency. Modern construction enables changing button settings and layouts for different tasks, whether for controlling heavy machines or game use.
The Importance of Contact and Switch Mechanisms
Contact and switching mechanisms are critically important for the proper operation of joysticks, as they affect their functionality and reliability. These mechanisms provide accurate engagement between user actions and device outputs. Therefore, exactitude becomes an essential factor in the operation of joysticks. For optimal longevity of the joystick, qualitative contact materials such as gold or silver alloys should be used as they provide the least resistance and wear. The switches themselves can be of different types: mechanical, membrane, or hall-effect sensors, depending on the application’s needs for sensitivity, endurance, resistance to the environment, etc. With these advancements, failure is less likely, and responsiveness is better, which is crucial in aviation and gaming, where real-time accuracy is critical.
Understanding Output and Input Systems
Input and output systems are integral to the interaction between users and machines. An input system receives information in the form of data or a signal from an individual or a surrounding setting and sends it to be processed. A keyboard, a mouse, a touch screen, and even sensors are good examples. They all convert physical activity and other external conditions into signals the machine understands.
Moreover, output systems convey information that has been processed to the user understandably. The most common include monitors, printers, speakers, and LEDs. These devices furnish information in graphical images and sounds, and even as physical objects, they make available feedback and outputs for the systems.
An example of an interaction interface in contemporary technology is a gaming console with a haptic feedback system. An input-output system applied in industry machines measures using specific sensors takes readings and processes the information to enhance the equipment’s functionality. Thus, seamless communication and efficiency are enabled in different applications and systems.
What Are the Applications of Industrial Joystick Controls?

Wherever adaptability and precision are placed as primary requirements, one comes across industrial joystick controls. These are integrated into heavy machinery like cranes, excavators, and forklifts, making it easy for operators to control movements accurately. Joysticks are also pivotal in automation systems where robotic arms and other automated mechanisms need precise handling. Moreover, these controls serve essential functions in the aerospace and marine framework, where navigation and operation movements must be done with utmost agility. Versatile and reliable, these tools are necessary in any industrial setup demanding intricate and fast operating machinery.
Use in Machinery and Industrial Operations
Maneuverability and control of assorted chores are effortless with joysticks as they function as control levers on industrial machinery. Operating cranes, forklifts, and excavators becomes easy since these enable an operator to control heavy loads with precision and minimal effort. CNC machines and welding systems also employ joysticks for seamless interface and precise alterations. In robotics, joysticks move robotic arms with high precision in assembly, packaging, and material handling, all of which are crucial actions that robotic arms perform. Joysticks make controlling faster and easier, significantly improving industrial output and efficiency.
Applications in Crane and Vehicle Controls
Joysticks are vital in controlling cranes and vehicles as they provide operators with a precise, intuitive, and ergonomic method of controlling heavy machinery. They are mainly designed for complex motion tasks like lifting, rotating, and positioning loads. In cranes, advanced joysticks have proportional control options, allowing smooth and precise movement and increasing safety and efficiency on construction sites. Likewise, joysticks enable multi-directional movements in excavators and forklifts, allowing for easier maneuvering in confined spaces or rough terrains. Modern technologies also add touch and wireless controls, enhancing performance and reducing operator strain. These qualities make joysticks critical in both mobile and stationary industrial equipment.
Role in Electric and Electronic Systems
Joysticks allow for effortless and accurate control over complex electric and electronic systems. They facilitate the transformation of mechanical movement into electrical signals. This feature makes modern joysticks applicable to video game consoles, drones, robots, and industrial machines and systems. Modern joysticks are equipped with potentiometer sensors, Hall effect sensors, or strain gauges that detect movement and direction for more efficient operation. These sensors transform inputs into commands that the systems can act upon almost instantly. Integrating microcontrollers and wireless controllers into robotics has made them more responsive and helpful for remote control and automation. Overall, joysticks operate as an interface between a human and a machine. Their versatility allows them to be applied throughout various fields of electronics and electricity.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Joystick for Your Needs?

In what order should one approach the selection of an industrial joystick? First, figure out the characteristics needed for the joystick to operate, which includes the environment in which it will function, be it harsh outdoor or cleanroom settings. Moreover, check the joystick’s IP rating and its resistance to dust, water, and other extreme temperatures for durability. After that, determine the functionality required, like several axes for movement, additional buttons, and analog versus digital output. And lastly, ensure that the existing hardware and software integrate seamlessly, looking at compatibility with other interfaces and protocols used. From here, think about operational customization on top of ergonomics for comfort. Work directly with manufacturer and supplier representatives, who are most equipped to offer creative solutions tailored to your specifications.
Evaluating Product Specifications and Features
While analyzing joysticks’ technical specifications and features, it is necessary to narrow down key areas of interest to make an accurate selection. Determine how the joystick receives analog or digital input and check operations requirements. Evaluate the number of axes and buttons for appropriateness with the functional requirements. Determine the type of connectivity; check the available ports, whether they are USB, Bluetooth, or any other proprietary connections, and ensure that they can interface with your system. Investigate the different brands and their user reviews to evaluate the quality of construction, average span, and product reliability under numerous conditions. Customization options and ergonomics should be tailored to the user’s preferences to minimize fatigue and maximize performance. Moreover, collaborate with the manufacturers or suppliers to guarantee all incorporations or sought modifications address operational needs.
Understanding the Number of Axis and Movement Capabilities
The number of axes in a joystick determines its versatility in movement and usage. For example, a single-axis joystick can only move forward or backward. In contrast, a dual-axis joystick can move forward, backward, and left and right, which helps control vehicles or machinery. More advanced three-axis joysticks can add rotation or vertical movement and are often used in drones, 3D modeling, and robotics.
While selecting a joystick, ensure that it meets the needs of the task or activity you are trying to accomplish and that the axe configuration matches your needs. Multi-axis joysticks are known to provide better control and flexibility, but they may be more challenging to use and more expensive. Ensure that the device has the required level of accuracy and takes action in all possible movements so performance is optimal.
Considering Reliability and Safety Features
While analyzing the reliability and safety ergonomics of a joystick, pay attention to the steps taken towards consistency of performance, including the use of fail-safe mechanisms and overall device durability. Assess if the casing is made to withstand wear and tear since it, along with the components, determines the longevity of reliable operation. Safety features such as redundant circuitry or fail-safe constructions are essential in critical domains like industrial machinery and aviation. Furthermore, the joystick must be checked to ensure it complies with applicable industry laws and claims, such as ISO 26262 – Functional Safety or CE marking, indicating conformity. From your side, regular maintenance, servicing, and software upgrades make the device safer and more reliable.
What Are the Recent Innovations in Industrial Joystick Technology?

Today’s technological advancements focus more on durability, precision, and user experience towards industrial joysticks. Sensors used in the device have been upgraded from mechanical components to Hall effect sensors, which are more accurate, precise, and reliable. Moreover, customizable settings, haptic feedback, wireless controls, and ergonomic features enhance operator comfort and efficiency. Growing issues towards real-time data monitoring and integration into innovative systems have made IoT and wireless connection necessary. In addition, heavy-duty designs with protective components such as IP-rated enclosures allow joysticks to function in extreme climates, which broadens their use in various industrial fields.
Advancements in Precision and Function
Today’s joysticks used in industrial work have drastically developed due to sensor technologies and user-friendly design advancements. For instance, Hall effect sensors offer the highest reliability since they utilize magnetic fields for joystick movement detection, meaning no contact interpretation, which eliminates damage. Furthermore, multi-axis controls permit the simultaneous use of several functions, especially in complicated machinery like cranes or robotic arms. Improved programmability allows operators to tailor input settings to specific organizational needs, optimizing workflows and minimizing idle time. These factors transform industrial joysticks into highly dependable components with precise and flexible functionalities tailored to rigorous conditions.
Integration of Control Devices and Systems
The combination of control devices and systems refers to consistently merging hardware with software to increase efficiency and automation in operations. In modern industrial operations, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) are often used with industrial joysticks to form an all-inclusive control system. These systems enable efficient data exchange, accurate motion control, and sophisticated safety features. Moreover, wireless technologies, IoT devices, and other advancements in connectivity facilitate remote monitoring and diagnostics, which reduces maintenance costs and downtime. Furthermore, the seamless merging of control devices guarantees machinery and software interaction, which helps simplify complex procedures and enhances the optimization of production workflows.
Trends in Custom and Ideal Solutions
Like any other industry, new approaches to control systems solutions are being shaped by technology. A significant trend is the growing need for modular, scalable systems that enable companies to modify their machinery or workflows as needs change. Custom automation solutions are being built to efficiently satisfy specific operational needs while allowing sufficient flexibility.
In other technologies, the integration of AI with predictive maintenance and performance optimization is drastically expanding. Because of these technologies, systems can adapt with accurate composite adjustments and learned data, minimizing the chances of unscheduled downtime.
Innovation in custom solutions, such as frameworks that reduce carbon footprint while ensuring optimal production standards, is gaining traction. This reflects global efforts to combat climate change.
In addition to these custom solution needs, a growing research focus is devoted to cyber-physical systems and data security. These changes highlight the need for custom attention and responsible, eco-friendly approaches to modern control systems.
References
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the different types of industrial joystick controls available?
A: Industrial joystick controls come in many types, including single-axis, dual-axis, and multi-axis joysticks. Each type is designed for various applications and can be customized to meet specific operational needs.
Q: How do momentary control switches function in joystick controls?
A: Momentary control switches in joysticks are designed only to remain active while pressed. Once released, they return to their original position, allowing for precise control in applications requiring quick, temporary actions.
Q: What are the typical applications of industrial joystick controls?
A: Industrial joystick controls are used in various applications, including heavy machinery operation, arcade game controls, robotics, etc. Their high reliability and long-lasting operational life make them suitable for demanding environments.
Q: How can joystick controls be customized for specific applications?
A: Joystick controls can be customized by choosing specific stick types, control switches, and additional features such as voltage ratings and protection levels. An engineering team can help tailor these components to meet unique industry needs.
Q: What innovations are available in modern joystick controls?
A: Modern joystick controls offer innovations like high-quality materials, enhanced protection features, and advanced electronic components, which improve their durability and performance in a wide range of industrial settings.
Q: How does one ensure the high reliability of joystick controls?
A: High reliability can be ensured by selecting joysticks with a long operational life, using high-quality materials, and installing them correctly. Regular maintenance and consulting with professionals like Contact p3 America can also enhance reliability.
Q: What is the significance of the 10k voltage rating in joystick controls?
A: The 10k voltage rating refers to the electrical resistance in the joystick’s potentiometers. This resistance is crucial for accurate speed and position control and ensures the joystick can handle various operational conditions.
Q: How are industrial joysticks protected against harsh environments?
A: Joysticks have protection features such as sealed enclosures, durable materials, and coatings that resist moisture, dust, and other environmental factors, ensuring consistent performance in harsh conditions.
Q: Can joystick controls be used in horizontal applications?
A: Yes, joystick controls can be installed for horizontal applications. They are designed to function effectively in various orientations, providing flexibility in their installation and use.
Q: Where can one shop for industrial joystick controls?
A: Industrial joystick controls can be purchased from specialized retailers or manufacturers. Companies with extensive industry experience often offer various options and customization services for specific needs.